

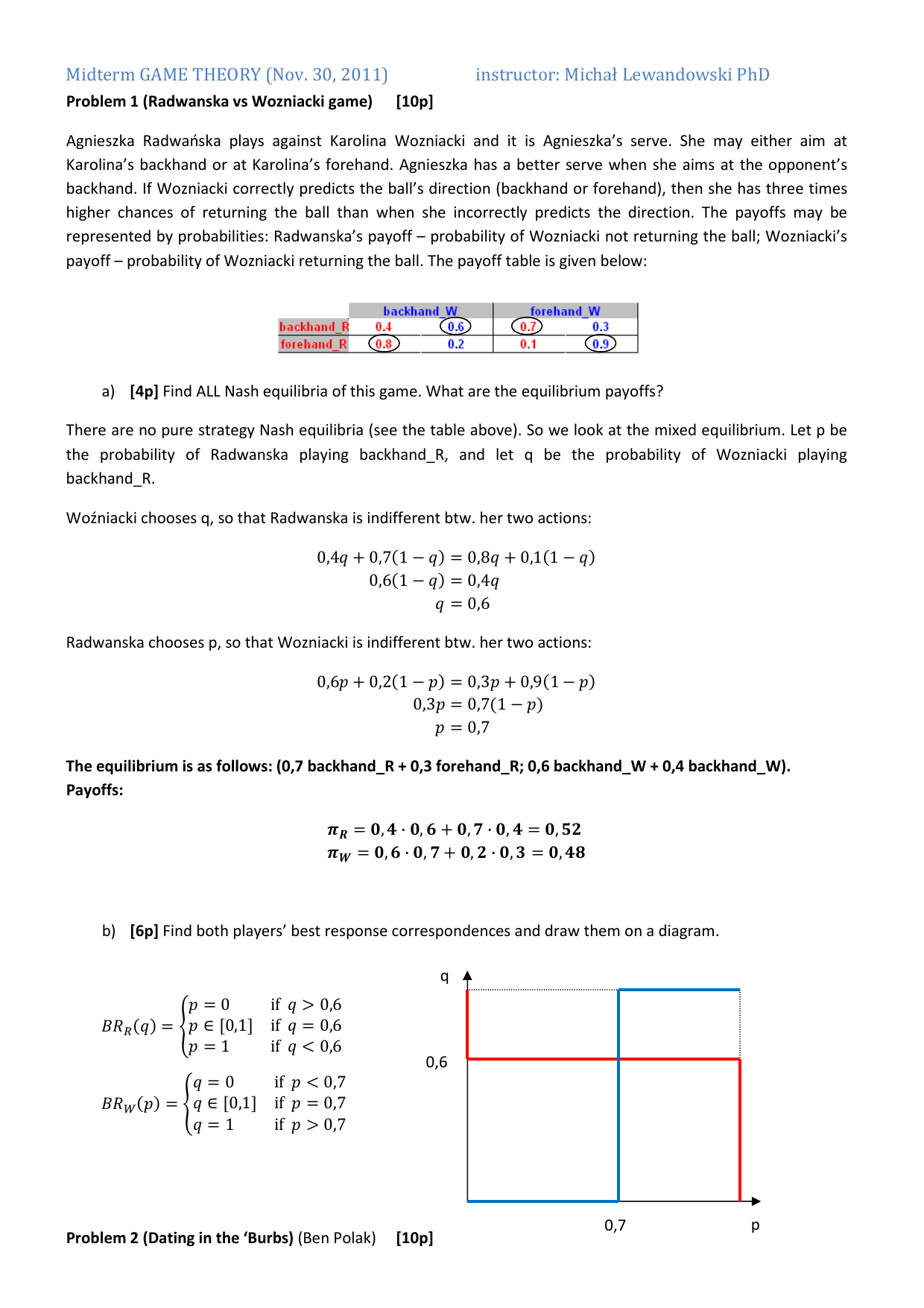
10 drops of 0.1 molar silver nitrate solution were added one drop at a time, and the color of the solution was noted. A sealed Beral pipet containing some of the alcoholic cobalt chloride-water system was obtained and the large end of the pipet was immersed in some hot water and the color change was noted. The strategy pair associated with (0,0) e. There is no pure strategy Nash equilibrium 2) What is true about dominant strategies in the game? 'Run' and 'Run Defense' are the dominant. Δn = 2- (3+1) = -2 Example: A mixture of nitrogen and hydrogen in a reaction vessel is allowed to attain equilibrium at 472°C. The equilibrium mixture of gases was analyzed and found to contain 0.127 M H2, 0.0402 M N2, and 0.00272 M NH3. From this data calculate Kc. Then, using the value for Kc calculate Kp.
We can relate the equilibrium constant of a chemical equilibrium to the rates of the forward and reverse reactions. For example, consider the process A ⇔ B. The rate of the forward reaction, A → B, is kf[A], where the little 'f' after the k denotes the rate constant for the forward reaction. Likewise, the rate of the reverse reaction, B → A, is kr[B], where 'r' denotes the rate constant for the reverse process. Since at equilibrium, the rates for the forward and backward reactions are the same (kf[A] = kr[B]), we can say that the equilibrium constant, Keq, is equal to [B]/[A] and kf/kr.
Keq is a neat constant because it allows us to determine the ratios of the concentrations of each chemical species in the equilibrium, which is pretty handy for reasons we'll see in this example:
Be careful not to mistake the equilibrium constant Keq Wolf forms 2 36 – create php web forms fillable. for the rate constant k! Keykey 2 6 – typing tutor test.
Solution: Let's walk through this problem step by step. The first step is to write the equilibrium expression for this process:
Problem 1: Given the reaction H2 + I2 ⇔ 2 HI, find the following:
a) The general expression for the equilibrium constant.
b) The equilibrium concentration of HI if I start with 2.00 M H2 and 2.00 M I2 and the equilibrium constant is 5.00.
eq values are very small. If Keq is small, then we can safely guess that the amount of product formed (x) will be very, very small when compared to the initial quantity of the reactant. This is because a very small Keq value means that very little product has been formed. As a result, we can omit the 'x' in the denominator to simplify the [1.00 - x] term because [1.00 - x] will be roughly equal to 1.00. Our new (and easier) expression to solve is transformed into:
Cyberline racing 1 0.
© 2003 by Ian Guch. All rights reserved including the right of reproduction in whole or in part in any form. Used by arrangement with Alpha Books, a member of Penguin Group (USA) Inc. Cat th460 parts manual.
Networker (show network information in menu bar) 2 0 3. To order this book direct from the publisher, visit the Penguin USA website or call 1-800-253-6476. You can also purchase this book at Amazon.com and Barnes & Noble.
Let's take a generic chemical equilibrium to try and determine what an equilibrium constant equal to 1 would mean. So,
The equilibrium constant for this reaction can be written as
Since the expression of the equilibrium constant depends on the equilibrium concentrations of both the reactans, and the products, we can determine that
What this means is that the reactions favors neither products, nor reactants, and that the equilibrium will be reached as an intermediate mixture , i. e. the concentrations of the products and of the reactans will be the same.
By comparison, the higher the equilibrium constant is above 1, the greater the concentrations of the products relative to the reactans. The smaller this value is, as a fraction between 0 and 1, the greater the concentrations of the reactans relative to the products.
